Slope Specialist Community
Our community is dedicated to building a professional, innovative, and sustainable platform for knowledge exchange.
We bring together experts in slope engineering, engineers, and academic researchers to share insights and ideas,
collectively promoting accurate slope stability analysis and safety maintenance principles.
Our goal is to achieve "professional sharing, innovative collaboration, and sustainable legacy."
Service Overview
服務介紹
Slope reinforcement optimization
邊坡補強方案最佳化
Providing optimal displacement-based solutions
for natural and reinforced slopes
Back-Analysis of Engineering Parameters
反算分析與工程參數優化
Back-calculating slope material strengths, reducing the cost and uncertainty associated with sampling
Comparative Evaluation of Retaining Structures
擋土結構設計評估
Optimizing retaining structures by assessing slope stabilization methods
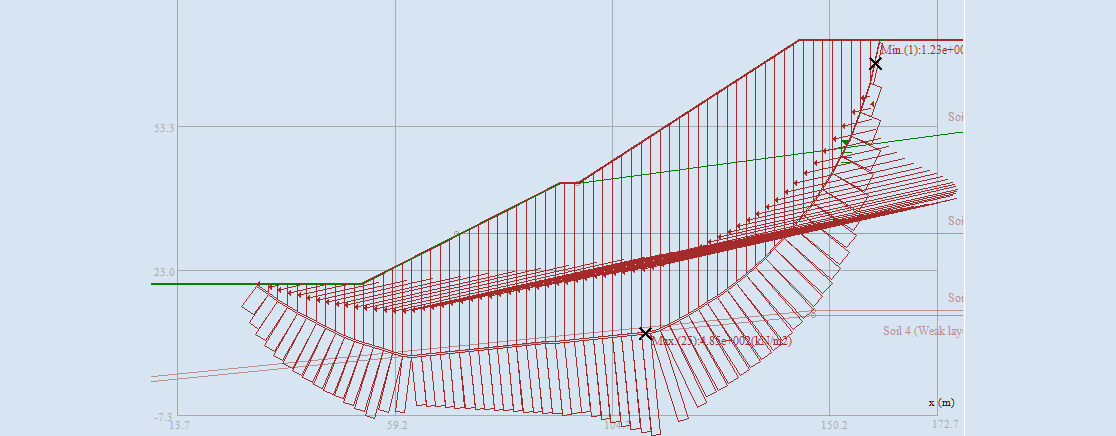
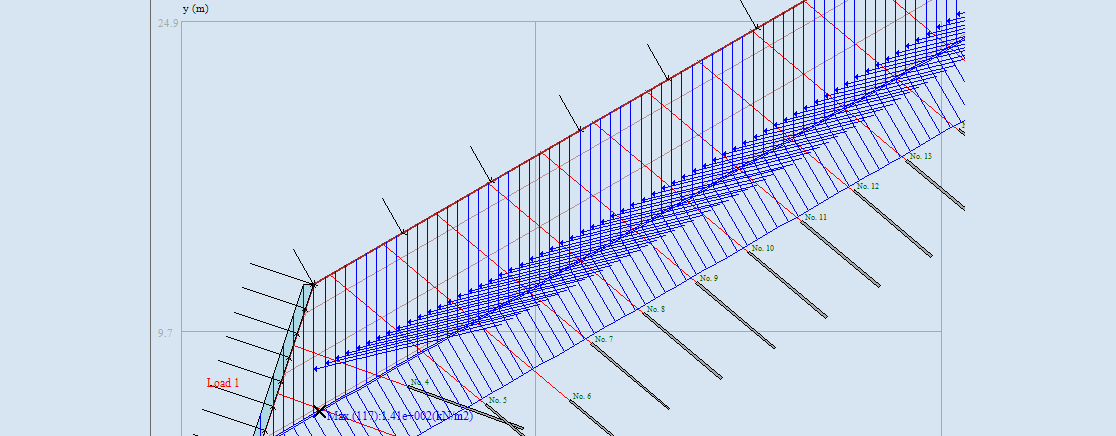
SLOPE-ffdm Overview
工具簡介

To transcend the limitations of traditional limit-equilibrium-based slope stability analysis methods, the Force-equilibrium-based Finite Displacement Method (FFDM) was developed in 2012 by Dr. C.-C. Huang at the Department of Civil Engineering, National Cheng Kung University in Tainan, Taiwan. FFDM transforms conventional slope stability analysis into a displacement-based approach by integrating a stress-displacement constitutive law into the force equilibrium of sliced soil masses.
FFDM serves as the core of the previous iteration of SLICE-DISP program, which has been employed in preliminary studies on groundwater-table-induced slope displacements. Follow-up experimental studies, including direct shear tests and back-analyses of slope failures, have further validated FFDM’s effectiveness in predicting slope displacements caused by internal and external factors.
Web News
網站訊息
邊坡穩定與變位分析工作坊
工作坊主旨 以極限平衡法(Limit Equilibrium) 進行邊坡穩定相關之工程設計與分析已超過百年的歷史。在極限平衡之 邊坡穩定分析中雖能獲得邊坡之安全係數依賴經驗操作之體系因其基於眾多之假設故以安全係數之邊坡穩定判斷為一過度不符合以變位為基準之現代化邊坡設計思維。
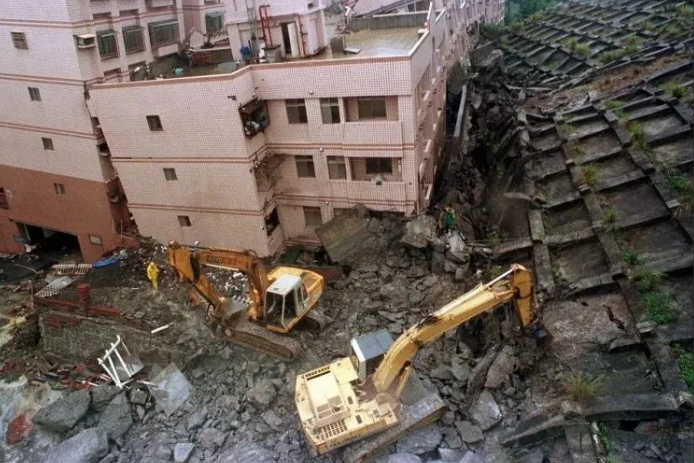
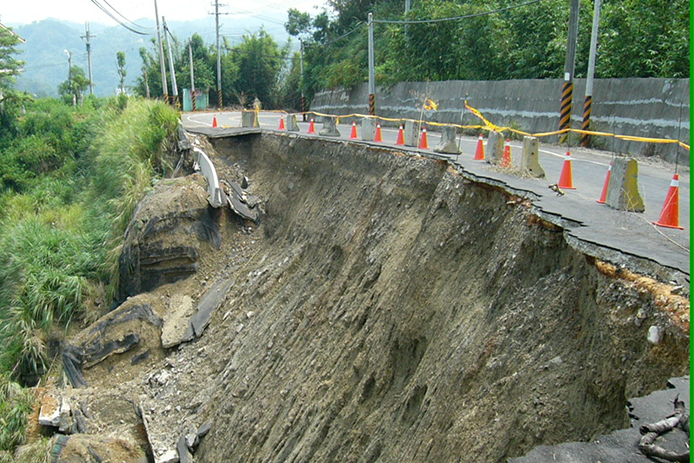
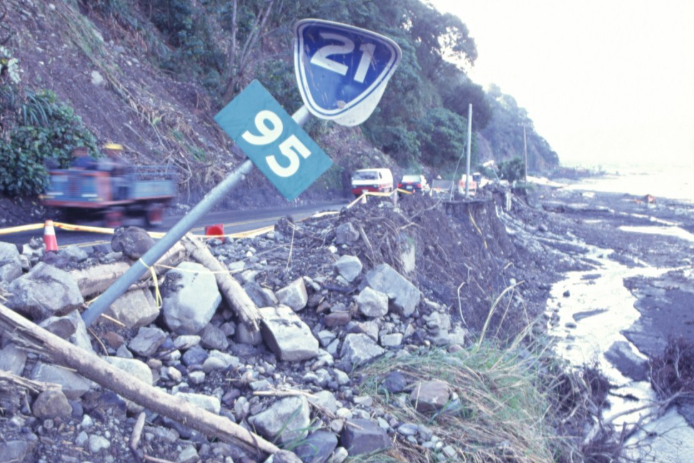
Mitigation of Slope Failures
邊坡災害與防治
Licensing and Pricing Plans
用戶方案
SLOPE-ffdm 2.0 offers flexible pricing plans tailored to meet the needs of individual users, corporate clients, and educational institutions. Each plan provides varying levels of licensing, technical support, and consulting services to optimize analytical accuracy and quality
Individual Plan
個人方案
For professionals, educators
and researchers
- 1. Personal license for independent use.
- 2. Licensed for one user
- 3. Standard technical support
(email assistance, troubleshooting). - 4. Regular software updates and patches.
- 5. Guidance on improving analytical output.
- 6. Special upgrade offer.
- 299 USD / Year
- 新台幣 9,000 / 年
- Subscribe Now
Corporate Plan
企業方案
For enterprise, corporation,
and professional teams
- 1. Multi-user licensing
- 2. Licensed for up to 2 users
- 3. Priority technical support (email assistance, troubleshooting, faster response time)
- 4. Regular software updates and patches.
- 5. Guidance on improving analytical output.
- 6. Special upgrade offer.
- 399 USD / Year
- 新台幣 12,000 / 年
- Subscribe Now
Educational plan
教室方案
(停售/Currently unavailable)
For non-profitable educational
or research institution
- 1. Multi-user educational licensing
- 2. Dedicated support for instructors and
administrators. - 3. Educational resources and training materials.
- 4. Regular software updates and patches.
- 5. Special upgrade offer.
- 499 USD / Year
- 新台幣 15,000 / 年
- Subscribe Now